What is SysML®?

The OMG Systems Modeling Language™ (OMG SysML®) is a general-purpose graphical modeling language for specifying, analyzing, designing, and verifying complex systems that may include hardware, software, information, personnel, procedures, and facilities. In particular, the language provides graphical representations with a semantic foundation for modeling system requirements, behavior, structure, and parametrics, which is used to integrate with other engineering analysis models. It represents a subset of UML 2 with extensions needed to satisfy the requirements of the UML™ for Systems Engineering RFP as indicated in Figure 1. SysML leverages the OMG XML Metadata Interchange (XMI®) to exchange modeling data between tools, and is also intended to be compatible with the evolving ISO 10303-233systems engineering data interchange standard.
The UML for Systems Engineering RFP was developed jointly by the OMG and the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) and issued by the OMG in March 2003. The RFP specified the requirements for extending UML to support the needs of the systems engineering community. The SysML Specification was developed in response to these requirements by the diverse group of tool vendors, end users, academia, and government representatives. The Object Management Group announced the adoption on July 6, 2006 and the availability of OMG SysML™ v1.0 in September 2007.
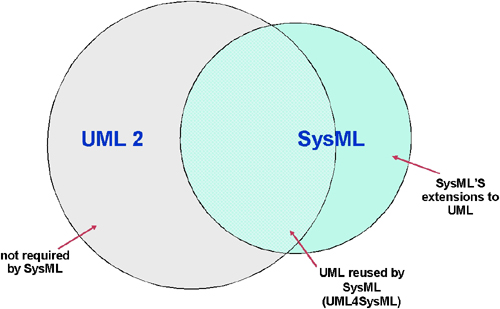
Figure 1. Relationship between SysML and UML
SysML Diagram Summary
The SysML diagram types are identified in Figure 2 and summarized below. Refer to the OMG SysML Tutorial for an overview of the language. (Note: Because these are large files, it is recommended that you save to your desktop by right clicking and save target)
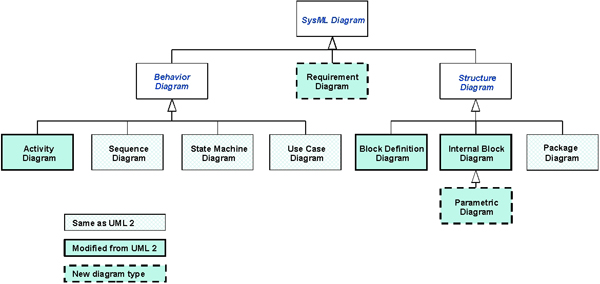
Figure 2. SysML Diagram Types
The block is the basic unit of structure in SysML and can be used to represent hardware, software, facilities, personnel, or any other system element. The system structure is represented by block definition diagrams and internal block diagrams. A block definition diagram describes the system hierarchy and system/component classifications. The internal block diagram describes the internal structure of a system in terms of its parts, ports, and connectors. The package diagram is used to organize the model.
The behavior diagrams include the use case diagram, activity diagram, sequence diagram, and state machine diagram. A use-case diagram provides a high-level description of functionality that is achieved through interaction among systems or system parts. The activity diagram represents the flow of data and control between activities. A sequence diagram represents the interaction between collaborating parts of a system. The state machine diagram describes the state transitions and actions that a system or its parts perform in response to events.
SysML includes a graphical construct to represent text based requirements and relate them to other model elements. The requirements diagram captures requirements hierarchies and requirements derivation, and the satisfy and verify relationships allow a modeler to relate a requirement to a model element that satisfies or verifies the requirements. The requirement diagram provides a bridge between the typical requirements management tools and the system models.
The parametric diagram represents constraints on system property values such as performance, reliability, and mass properties, and serves as a means to integrate the specification and design models with engineering analysis models.
SysML also includes an allocation relationship to represent various types of allocation, including allocation of functions to components, logical to physical components, and software to hardware.
A simple example of some of the key diagram types is highlighted in Figure 3.
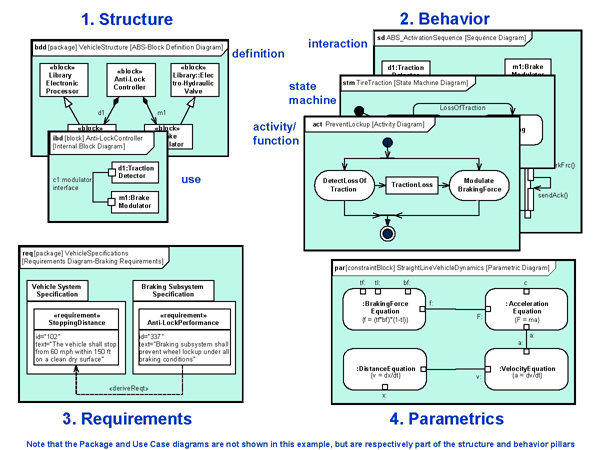
Figure 3. The Four Pillars of SysML
The OMG SysML Specification includes diagram element tables in chapters 7-17 that identifies allowable symbols on each of the diagram types, as well as usage examples. Fragments corresponding to the design of a hybrid sports utility vehicle (HSUV) are included in the sample problem in Annex D of the specification.
The OMG SysML Specification Version 1.4.1 is also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as a full International Standard (IS), whose short title is “ISO/IEC 19514:2017” and full title is "ISO/IEC 19514:2017, Information technology -- Object management group systems modeling language (OMG SysML)". The direct catalogue reference is https://www.iso.org/standard/65231.html.